3.1 Energy Principles
What is Energy?
Energy is the ability to do work. It is a scalar quantity measured in joules (J). Energy is not "used up"; it is just transferred from one store to another.
Energy is the ability to do work. It is a scalar quantity measured in joules (J). Energy is not "used up"; it is just transferred from one store to another.
⚡ Key Concept:
The Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred, stored, or dissipated (spread out).
• Total energy in a closed system stays constant
• Energy just moves between different stores
• "Using" energy really means transferring it
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred, stored, or dissipated (spread out).
• Total energy in a closed system stays constant
• Energy just moves between different stores
• "Using" energy really means transferring it
💡 What is a System?
A system is just a word for the object or group of objects we are looking at.
A closed system is one where no energy can enter or leave.
Examples:
• A bouncing ball (ball + Earth)
• A kettle heating water (kettle + water)
• A car braking (car + brakes + surroundings)
A closed system is one where no energy can enter or leave.
Examples:
• A bouncing ball (ball + Earth)
• A kettle heating water (kettle + water)
• A car braking (car + brakes + surroundings)
Energy In
100 J
Chemical energy from fuel
Energy Out
100 J
Kinetic + Thermal energy
Energy in always equals energy out
How Energy is Stored
There are 8 main ways energy can be stored. You need to know all of them.
There are 8 main ways energy can be stored. You need to know all of them.
Kinetic
Energy of a moving object
Gravitational Potential
Energy due to height
Elastic Potential
Stretched or squashed objects
Thermal
Energy due to temperature
Chemical
Energy in chemical bonds
Nuclear
Energy in atomic nuclei
Magnetic
Repelling magnets pushed together
Electrostatic
Repelling charges pushed together
Example: Energy Stores in Everyday Objects
| Object | Energy Store | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Moving car | Kinetic | It's moving |
| Book on a shelf | Gravitational Potential | It's above the ground |
| Stretched rubber band | Elastic Potential | It's stretched |
| Hot cup of tea | Thermal | It's hot |
| Battery | Chemical | Energy in chemical bonds |
🎯 Energy Store Identifier
How Energy Moves Between Stores
Energy is moved from one store to another through one of four pathways:
Example: Pushing a box (work done)
Example: Current in a wire
Example: Kettle heating water
Example: Light from the Sun
Energy is moved from one store to another through one of four pathways:
Mechanically
A force moves an objectExample: Pushing a box (work done)
Electrically
Charge moves through a potential differenceExample: Current in a wire
By Heating
Energy from hot to cold objectExample: Kettle heating water
By Radiation
Energy transferred by wavesExample: Light from the Sun
Example: Energy Transfer Diagram
Situation: A ball is thrown upwards
Kinetic Store
(moving hand)
→
(moving hand)
Mechanically
(force on ball)
→
(force on ball)
Kinetic Store
(moving ball)
→
(moving ball)
GPE Store
(ball at height)
(ball at height)
Example: Light Bulb Energy Transfer
Chemical Store
(power station fuel)
→
(power station fuel)
Electrically
(current in wires)
→
(current in wires)
Light + Thermal
(bulb)
(bulb)
🎯 Energy Transfer Practice
Energy Equations
⚡ Kinetic Energy Formula:
$$KE = \frac{1}{2} \times m \times v^2$$
Where:
• $KE$ = Kinetic Energy in joules (J)
• $m$ = mass in kilograms (kg)
• $v$ = speed in metres per second (m/s)
Note: Velocity is squared, so doubling speed gives 4× the kinetic energy.
Where:
• $KE$ = Kinetic Energy in joules (J)
• $m$ = mass in kilograms (kg)
• $v$ = speed in metres per second (m/s)
Note: Velocity is squared, so doubling speed gives 4× the kinetic energy.
Example 1: Calculating Kinetic Energy
A car of mass 1200 kg travels at 15 m/s. Calculate its kinetic energy.
Step 1: Write the formula
$KE = \frac{1}{2} \times m \times v^2$
Step 2: Substitute values
$KE = \frac{1}{2} \times 1200 \times 15^2$
Step 3: Calculate
$KE = \frac{1}{2} \times 1200 \times 225$
$KE = 600 \times 225$
$KE = 135,000$ J = 135 kJ
Step 1: Write the formula
$KE = \frac{1}{2} \times m \times v^2$
Step 2: Substitute values
$KE = \frac{1}{2} \times 1200 \times 15^2$
Step 3: Calculate
$KE = \frac{1}{2} \times 1200 \times 225$
$KE = 600 \times 225$
$KE = 135,000$ J = 135 kJ
⚡ Gravitational Potential Energy Formula:
$$GPE = m \times g \times h$$
Where:
• $GPE$ = Gravitational Potential Energy in joules (J)
• $m$ = mass in kilograms (kg)
• $g$ = gravitational field strength (9.8 N/kg on Earth)
• $h$ = height change in metres (m)
Where:
• $GPE$ = Gravitational Potential Energy in joules (J)
• $m$ = mass in kilograms (kg)
• $g$ = gravitational field strength (9.8 N/kg on Earth)
• $h$ = height change in metres (m)
Example 2: Calculating GPE
A 5 kg box is lifted 3 m onto a shelf. Calculate the GPE gained. (Use g = 10 N/kg)
Step 1: Write the formula
$GPE = m \times g \times h$
Step 2: Substitute values
$GPE = 5 \times 10 \times 3$
Step 3: Calculate
$GPE = 150$ J
Step 1: Write the formula
$GPE = m \times g \times h$
Step 2: Substitute values
$GPE = 5 \times 10 \times 3$
Step 3: Calculate
$GPE = 150$ J
💡 Energy Conversion: Ball Thrown Upwards
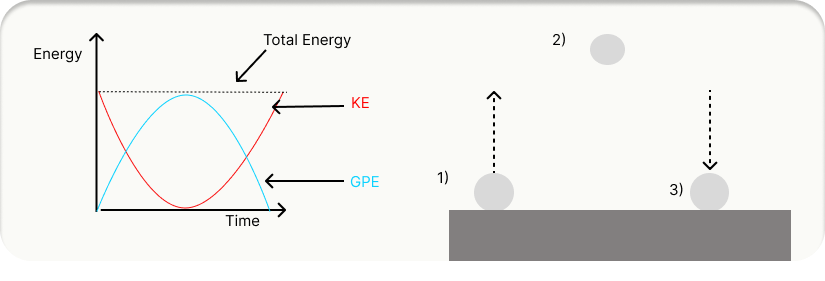 (1) Launch: Maximum KE, zero GPE
(1) Launch: Maximum KE, zero GPE
(2) Peak: Zero KE, maximum GPE
(3) Falling: GPE converts back to KE
Total energy stays constant throughout.
 (1) Launch: Maximum KE, zero GPE
(1) Launch: Maximum KE, zero GPE(2) Peak: Zero KE, maximum GPE
(3) Falling: GPE converts back to KE
Total energy stays constant throughout.
🧮 Energy Calculator:
Kinetic Energy
Mass: kg
Speed: m/s
Mass: kg
Speed: m/s
Gravitational PE
Mass: kg
Height: m
Mass: kg
Height: m
🎯 Energy Calculation Practice
J
J
Work Done
Work Done is the scientific term for energy transferred mechanically (by a force). When you push a box across the floor, you are doing work against the force of friction.
• Measured in joules (J)
• Energy transferred by a force
• Force must move the object
• Measured in watts (W)
• Rate of energy transfer
• Higher power = faster transfer
Work Done is the scientific term for energy transferred mechanically (by a force). When you push a box across the floor, you are doing work against the force of friction.
⚡ Work Done Formula:
$$W = F \times d$$
Where:
• $W$ = Work Done in joules (J)
• $F$ = Force in newtons (N)
• $d$ = Distance moved in the direction of force (m)
Remember: 1 joule = 1 newton × 1 metre
Where:
• $W$ = Work Done in joules (J)
• $F$ = Force in newtons (N)
• $d$ = Distance moved in the direction of force (m)
Remember: 1 joule = 1 newton × 1 metre
Example 1: Calculating Work Done
A person pushes a box with a force of 50 N for a distance of 8 m. Calculate the work done.
Step 1: Write the formula
$W = F \times d$
Step 2: Substitute values
$W = 50 \times 8$
Step 3: Calculate
$W = 400$ J
Step 1: Write the formula
$W = F \times d$
Step 2: Substitute values
$W = 50 \times 8$
Step 3: Calculate
$W = 400$ J
⚡ Power Formula:
$$P = \frac{E}{t}$$ or $$P = \frac{W}{t}$$
Where:
• $P$ = Power in watts (W)
• $E$ or $W$ = Energy transferred or Work done in joules (J)
• $t$ = Time in seconds (s)
Remember: 1 watt = 1 joule per second
Where:
• $P$ = Power in watts (W)
• $E$ or $W$ = Energy transferred or Work done in joules (J)
• $t$ = Time in seconds (s)
Remember: 1 watt = 1 joule per second
Example 2: Calculating Power
A motor transfers 6000 J of energy in 30 seconds. Calculate the power.
Step 1: Write the formula
$P = \frac{E}{t}$
Step 2: Substitute values
$P = \frac{6000}{30}$
Step 3: Calculate
$P = 200$ W
Step 1: Write the formula
$P = \frac{E}{t}$
Step 2: Substitute values
$P = \frac{6000}{30}$
Step 3: Calculate
$P = 200$ W
Example 3: Multi-Step Problem
A crane lifts a 200 kg load through 15 m in 10 seconds. Calculate the power of the crane. (Use g = 10 N/kg)
Step 1: Calculate work done (= GPE gained)
$W = m \times g \times h$
$W = 200 \times 10 \times 15 = 30,000$ J
Step 2: Calculate power
$P = \frac{W}{t} = \frac{30,000}{10} = 3,000$ W = 3 kW
Step 1: Calculate work done (= GPE gained)
$W = m \times g \times h$
$W = 200 \times 10 \times 15 = 30,000$ J
Step 2: Calculate power
$P = \frac{W}{t} = \frac{30,000}{10} = 3,000$ W = 3 kW
Work Done
• $W = F \times d$• Measured in joules (J)
• Energy transferred by a force
• Force must move the object
Power
• $P = E \div t$• Measured in watts (W)
• Rate of energy transfer
• Higher power = faster transfer
🎯 Work & Power Practice
Real Life Applications:
• Appliances: Power ratings tell you energy use (e.g., 2000 W kettle)
• Exercise: Calories burned = work done by muscles
• Vehicles: Engine power determines acceleration
• Electricity bills: You pay for energy (kWh), not power
• Sports: Faster athletes have more power output
• Appliances: Power ratings tell you energy use (e.g., 2000 W kettle)
• Exercise: Calories burned = work done by muscles
• Vehicles: Engine power determines acceleration
• Electricity bills: You pay for energy (kWh), not power
• Sports: Faster athletes have more power output